Ovulation Induction
It is an assisted reproduction method indicated to treat fertility problems in women who have irregular or absent ovulation.
Ovulation induction in anovulatory cycles
Ovulation induction is an assisted reproduction method indicated to treat fertility problems in women who have irregular or absent ovulation, due to hormonal imbalances or polycystic ovary syndrome.
What is ovulation induction
Ovulation induction is a simple procedure that assists in causing ovulation. In women who have absent ovulation, this pharmaceutical treatment aims to release a mature egg.
Ovulation induction is usually followed by intercourse, but is often part of other treatments, such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or IVF.
Once the drugs are administered, the ovaries are stimulated to increase the number of eggs that will be released per cycle. This maximizes the chance of conception during intercourse, IUI or IVF.
Treatment procedure
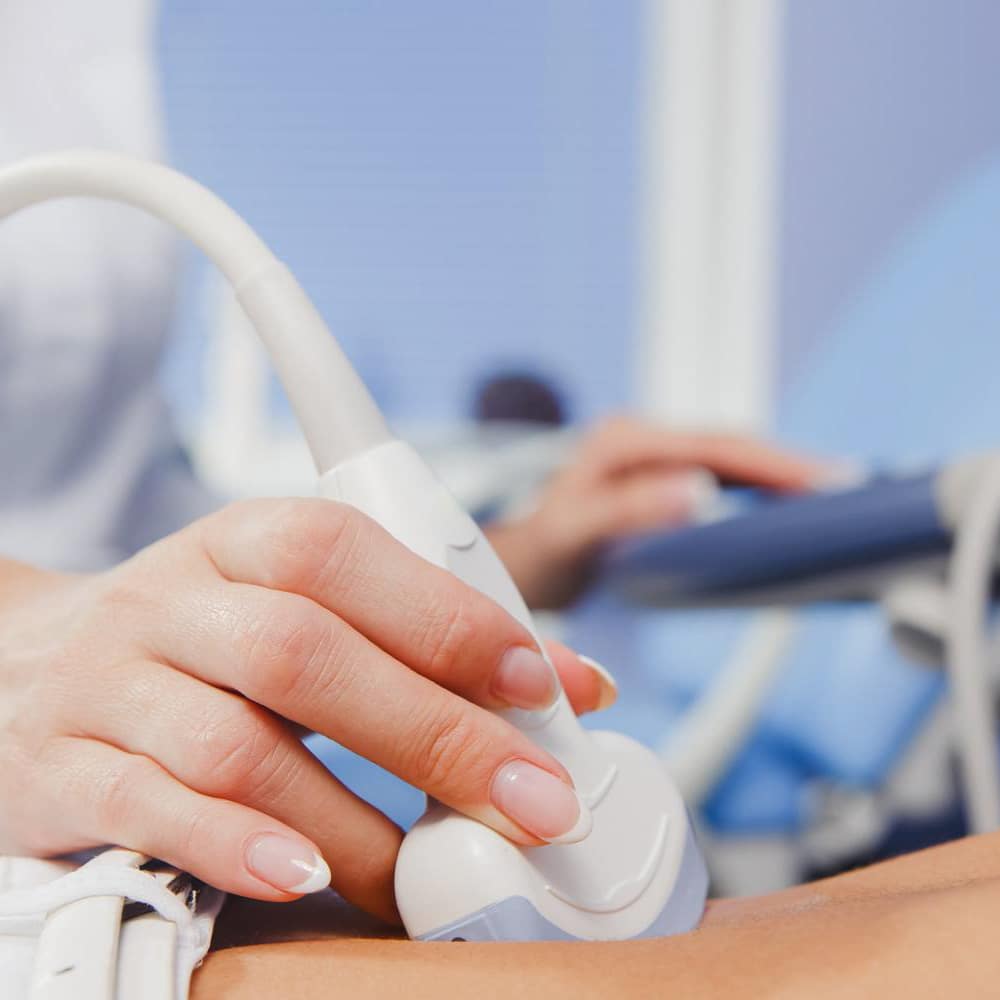
Initially, the doctor recommends special blood tests that measure the hormone levels at various stages of the woman’s cycle. These are followed by transvaginal ultrasounds to examine the development of the ovarian follicles, as well as the thickness and condition of the endometrium.
The procedure below is usually followed during ovulation induction:
In the first 2-3 days of the menstrual cycle, the woman undergoes blood tests and an ultrasound to examine whether the conditions are right for induction to begin. On the following day, the woman starts receiving pharmaceutical treatment. Depending on the ovulation induction method, ovulation follicle development is monitored with 2-4 transvaginal ultrasounds and the blood hormone levels may also be measured. The egg production process may be delayed in women with irregular menstrual cycle.
Once the ovarian follicles reach a satisfactory size, the day of the upcoming ovulation may either be predicted by the sudden increase in the luteinizing hormone (LH) levels in the blood or may be scheduled in advance with the administration of chorionic gonadotropin in the form of an injection, which causes final maturation of the ovarian follicles and ovulation. Around 32-36 hours after the increase in LH or the administration of the chorionic gonadotropin injection is the ideal time for the couple to have intercourse or for IUI to be performed.
Treatment duration
The treatment lasts from 10 to 20 days, depending on the treatment protocol used and the woman’s response to the specific method.
Usual pharmaceutical treatment
The pharmaceutical substance often used as the first choice to induce ovulation is citric clomiphene, which causes mild ovarian stimulation and does not have serious side-effects. It is administered orally in the form of pills for 5 consecutive days at the beginning of the woman’s cycle.
Another way to stimulate the ovaries and induce ovulation is to administer pharmaceutical substances known as gonadotropins, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These substances are produced naturally in the woman’s pituitary gland and act on the ovarian follicles, causing their growth and maturation.
Stimulation based on this method is used in women with absence of ovulation, due to absence of their own pituitary gland gonadotropins, and in women in whom ovulation induction with clomiphene did not yield satisfactory results.
The gonadotropins are administered daily in the form of injections, in small doses, starting from day 2 or 3 of the cycle. When gonadotropins are used to induce ovulation, the woman must be monitored closely, with consecutive ultrasounds and blood estrogen level measurements, as to avoid the risk of development of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome and multiple pregnancies.
Relevant Topics
-
Semi-Natural Cycle IVF / Mini IVF
Semi-Natural Cycle IVF / Mini IVF Mini-IVF or micro-IVF treatment is a minimum ovarian stimulation protocol during IVF. Mini-IVF...
-
Natural Cycle
Natural Cycle Natural-cycle IVF is a relatively simple procedure Natural-cycle IVF is a relatively simple procedure and consists of...
-
Ovulation Induction
Ovulation Induction It is an assisted reproduction method indicated to treat fertility problems in women who have irregular or...
-
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) The semen is treated in the lab, where active motile sperm is separated from sperm with...
-
In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) In-vitro fertilization (IVF) is a process whereby the eggs are fertilized by a sperm outside of...